C++ Recursion(How recursion works in C++)
C++ Recursion(How recursion works in C++)
A function that calls itself is known as recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
How recursion works in C++?
void recurse()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
The figure below shows how recursion works by calling itself over and over again.
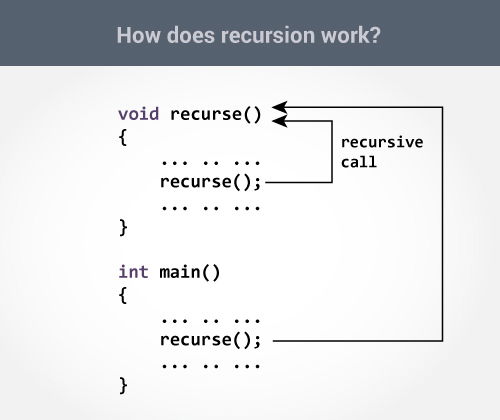
The recursion continues until some condition is met.
To prevent infinite recursion, if...else statement (or similar approach) can be used where one branch makes the recursive call and other doesn't.
Example 1: Factorial of a Number Using Recursion
// Factorial of n = 1*2*3*...*n#include <iostream>using namespace std;int factorial(int);int main(){int n;cout<<"Enter a number to find factorial: ";cin >> n;cout << "Factorial of " << n <<" = " << factorial(n);return 0;}int factorial(int n){if (n > 1){return n*factorial(n-1);}else{return 1;}}
Output
Enter a number to find factorial: 4 Factorial of 4 = 24
Explanation: How this example works?
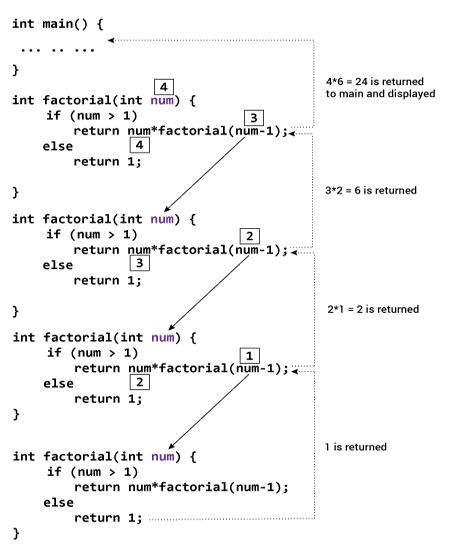
Suppose the user entered 4, which is passed to the
factorial() function.- In the first
factorial()function, test expression inside if statement is true. Thereturn num*factorial(num-1);statement is executed, which calls the secondfactorial()function and argument passed isnum-1which is 3.
- In the second
factorial()function, test expression inside if statement is true. Thereturn num*factorial(num-1);statement is executed, which calls the thirdfactorial()function and argument passed isnum-1which is 2.
- In the third
factorial()function, test expression inside if statement is true. Thereturn num*factorial(num-1);statement is executed, which calls the fourthfactorial()function and argument passed isnum-1which is 1.
- In the fourth
factorial()function, test expression inside if statement is false. Thereturn 1;statement is executed, which returns 1 to thirdfactorial()function.
- The third
factorial()function returns 2 to the secondfactorial()function.
- The second
factorial()function returns 6 to the firstfactorial()function.
- Finally, the first
factorial()function returns 24 to themain()function, which is displayed on the screen.




Comments
Post a Comment